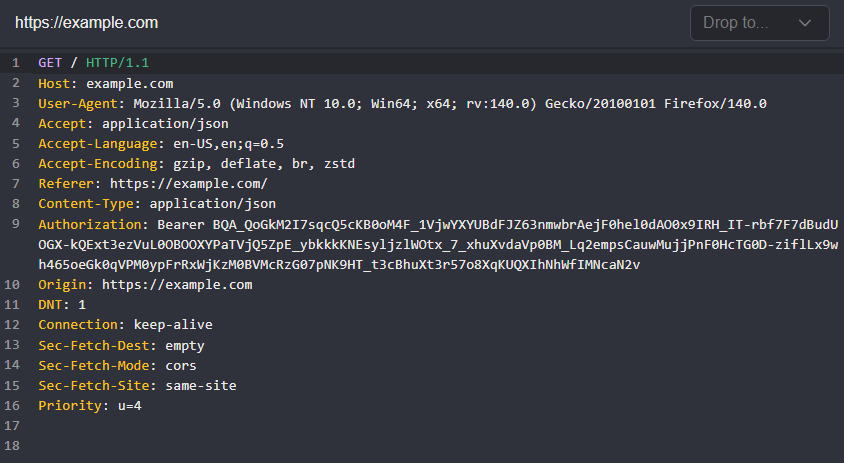
Refresh Authentication Workflow
In this tutorial, we will create a passive workflow that will automatically store and update either session cookies or tokens, as environment variables.
Then, by using placeholders in requests for the environment variables, you can achieve continuous, uninterrupted testing without manually updating expired sessions.
setVar()
The setVar() function sets an environment variable to a given value. It requires the following parameters:
name: The name of the environment variable.value: The value of the environment variable.secret: Determines if the environment variable is displayed as plaintext or masked.global: Determines if the envrionment variable is set globally or in the currently selected envrionment.
await sdk.env.setVar({
name: "session",
value: "123ABC321XYZ",
secret: true,
global: false
});INFO
If the name does not already exist, a new environment variable will be created. If the name matches an existing environment variable, its value will be overwritten.
TIP
To set the variable to a specific environment, use the env field and supply an existing environment name as its value:
env: "Demo Environment"This specification will take precedence over the global flag.
Creating a Passive Workflow
To begin, navigate to the Workflows interface, select the Passive tab, and click the + New workflow button.

Next, rename the workflow by typing in the Name input field. You can also provide an optional description of the workflow's functionality by typing in the Description input field.
Nodes and Connections
For both workflows, the overall node layout will be:
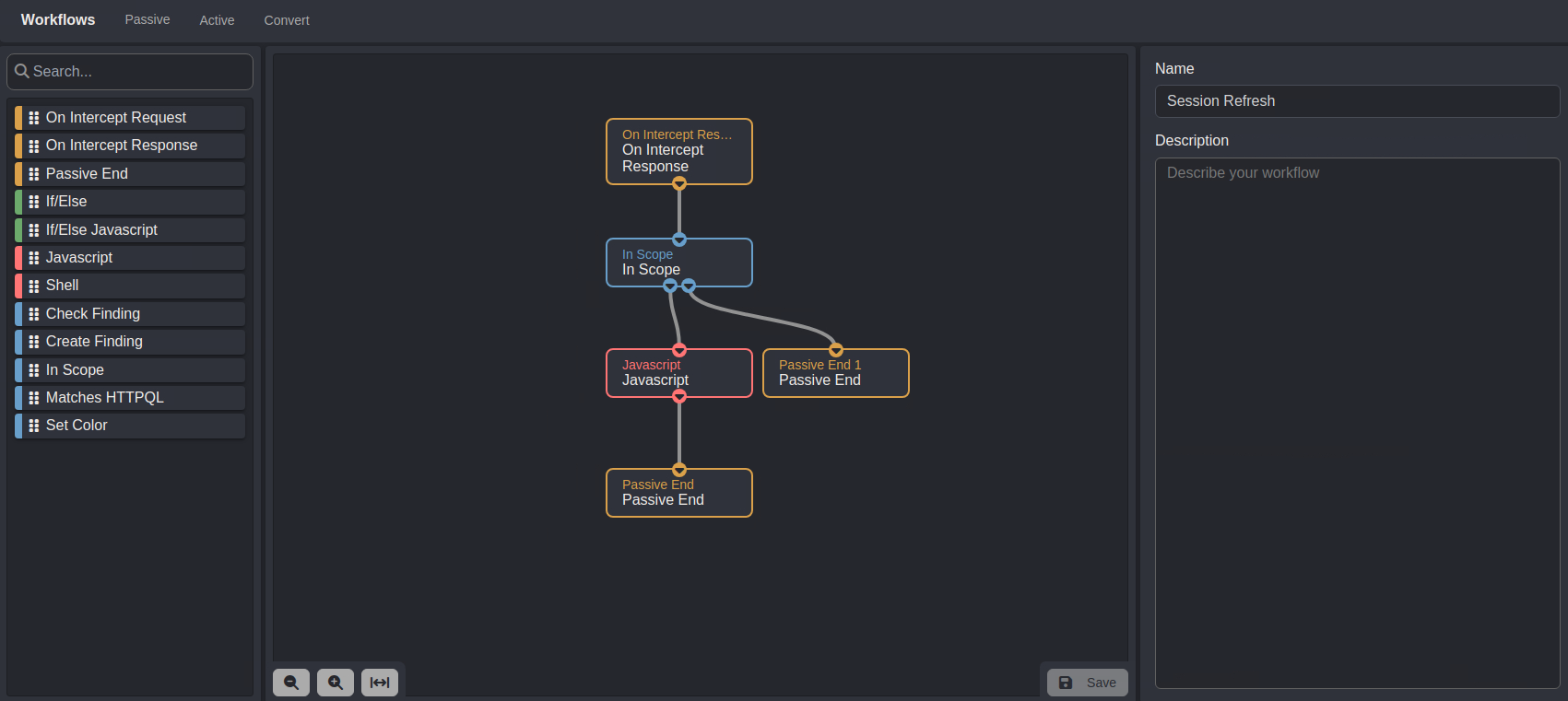
- The
On Intercept Responsenode outputs$on_intercept_response.requestand$on_intercept_response.responseobjects which represent proxied requests and their corresponding responses. - The
In Scopenode checks if the value of a request's Host header is included in the in-scope list of a scope preset. If it is not - the workflow will end. - In-scope request and response objects will be passed to the
Javascriptnode. - Once a request or response has been processed by the script in the
Javascriptnode, the workflow will end.
Session Cookies
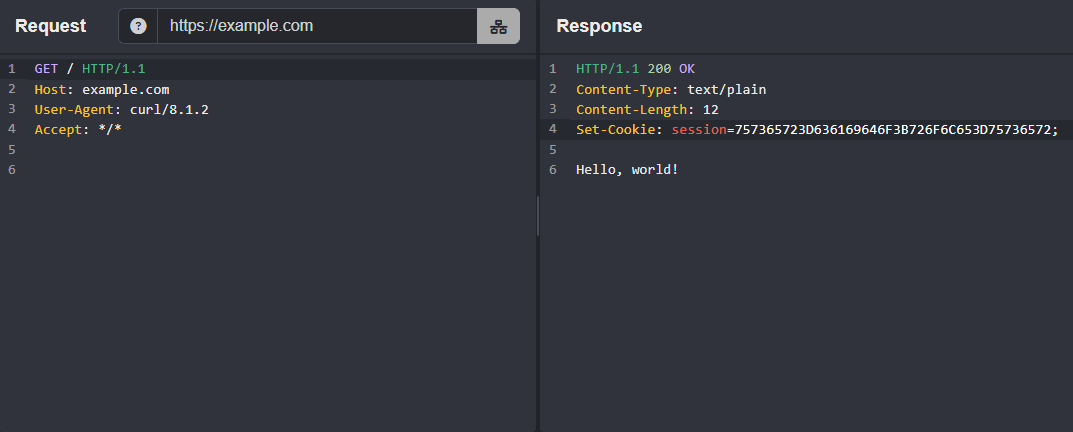
Consider a response to a successful credential submission that issues a session cookie via the Set-Cookie header:
Set-Cookie: session=757365723D636169646F3B726F6C653D75736572;Extracting a Session Cookie
- Click on the
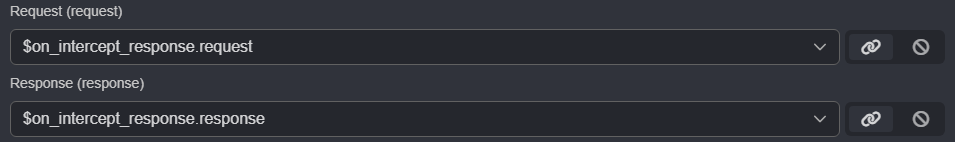
In Scopenode to access its editor and ensure the$on_intercept_response.requestobject is referenced as input data.

Close the editor window and click on the
Javascriptnode to access its editor.Then, click within the coding environment, select all of the existing code, and replace it with the following script:
export async function run({ request, response }, sdk) {
if (response) {
let cookie = response.getHeader("Set-Cookie");
if (cookie && cookie.length > 0) {
await sdk.env.setVar({
name: "session",
value: cookie.join("; "),
secret: false,
global: true
});
}
}
}- Reference the
$on_intercept_response.requestand$on_intercept_response.responseobjects as input data.
Once these steps are completed, close the editor window and click on the Save button to update and save the configuration.
Script Breakdown
First, an asynchronous function is defined that takes a request and response object pair and the sdk object as parameters. The script will execute every time an in-scope response object is passed from the In Scope node.
export async function run({ request, response }, sdk) {
if (response) {Then, using the .getHeader() method, the Set-Cookie header is extracted and stored in the cookie variable. If the header exists, the .setVar() method is used to set an environment variable.
let cookie = response.getHeader("Set-Cookie");
if (cookie && cookie.length > 0) {
await sdk.env.setVar({
name: "session",
value: cookie.join("; "),
secret: false,
global: true
});Testing the Workflow
To test the workflow:
Type in an in-scope domain in the connection URL input field.
Then, add a
Set-Cookie: session=<value>;header to the response.
- Next, click on the
Runbutton. A message will appear notifying you that the workflow executed successfully.

The Result
To view the set environment variable, navigate to the Environment interface and refresh the Global environment by clicking on its list row.
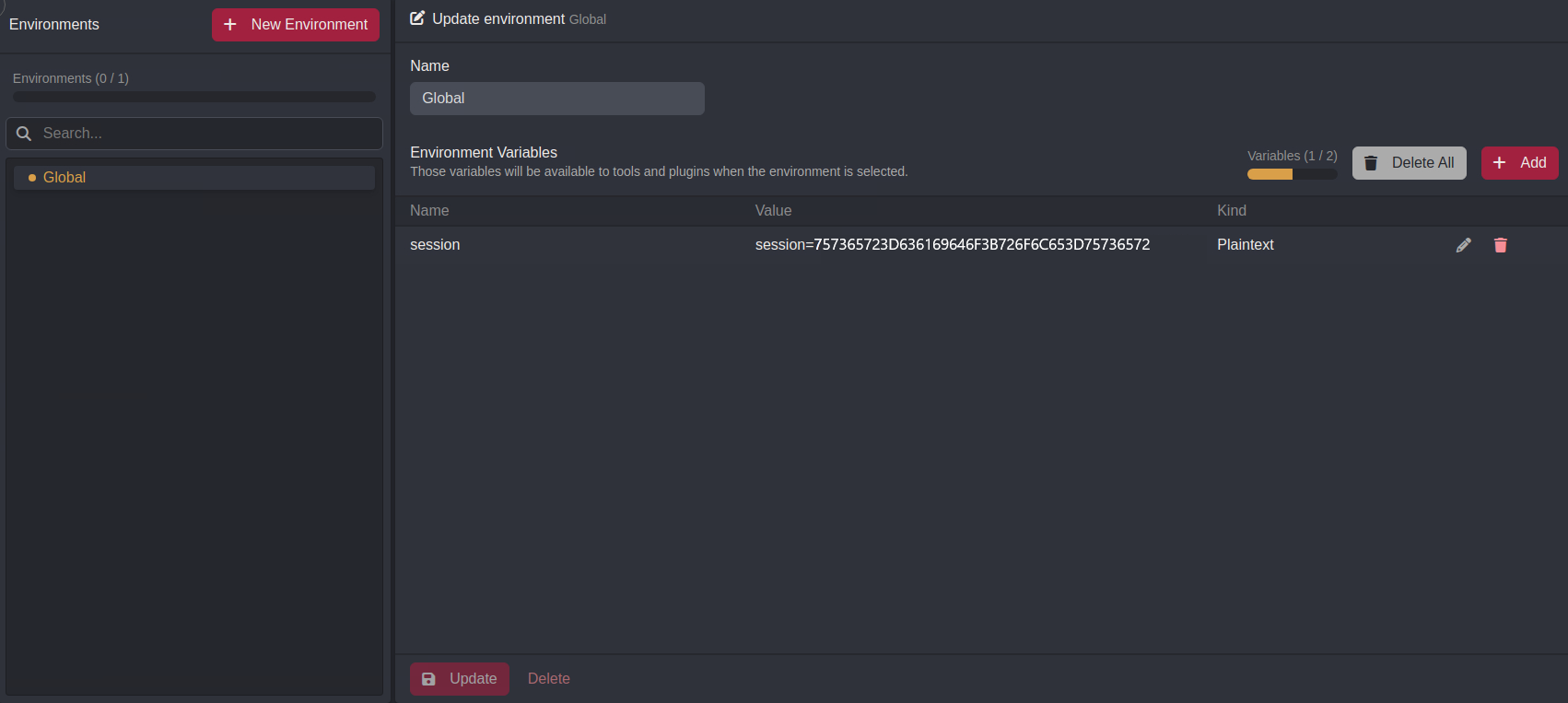
Session Tokens
Consider a response to a successful credential submission that issues a session token via an access_token JSON parameter:
{"access_token":"BQA_QoGKzM2I7sqcQ5cKB0oM4F_1VjwYXyUBdFJZ63nMwbrAejF0hel0dA0Ox9IRH_IT-rbt7F7dBudUOGX-kQExt3ezVuL0OBOOXYPaTVjQ5ZpE_ybkkKNEsyIjzIwOtx_7_xhuXvdaVp0BM_Lq2empsCauwvMujhPNf0HcTG0D-zIfLx9wh465oeGk0qVPM0ypFRxRWjkzM0BVMcRzG07pNk9HT_t3cBhuXt3r57o8XqKUQXlhNhWfMNca9N2v","token_type":"Bearer","expires_in":3600,"scope":"email"}Extracting a Session Token
- Click on the
In Scopenode to access its editor and ensure the$on_intercept_response.requestobject is referenced as input data.

Close the editor window and click on the
Javascriptnode to access its editor.Then, click within the coding environment, select all of the existing code, and replace it with the following script:
export async function run({ request, response }, sdk) {
const authFilter = `req.path.cont:"/auth" OR req.path.cont:"/login" OR req.path.cont:"/token" OR req.path.cont:"/oauth" OR req.path.cont:"/refresh"`;
if (sdk.requests.matches(authFilter, request, response)) {
let body = response.getBody();
if (body) {
let json = body.toJson();
let accessToken = json.access_token;
if (accessToken) {
await sdk.env.setVar({
name: "Bearer",
value: accessToken,
secret: false,
global: true,
});
}
}
}
}- Reference the
$on_intercept_response.requestand$on_intercept_response.responseobjects as input data.

Once these steps are completed, close the editor window and click on the Save button to update and save the configuration.
Script Breakdown
First, an asynchronous function is defined that takes a request and response object pair and the sdk object as parameters.
export async function run({ request, response }, sdk) {Using sdk.requests.matches() the execution of the script is scoped to common authentication endpoints with HTTPQL query statements. The script will execute every time an in-scope request object to one of these endpoints is passed from the In Scope node.
const authFilter = `req.path.cont:"/auth" OR req.path.cont:"/login" OR req.path.cont:"/token" OR req.path.cont:"/oauth" OR req.path.cont:"/refresh"`;
if (sdk.requests.matches(authFilter, request, response)) {Then, using the .getBody() method, we extract the response body and if it exists we parse it as JSON using .toJson(). If an access_token parameter exists, we use the .setVar() method to set an environment variable.
let body = response.getBody();
if (body) {
let json = body.toJson();
let accessToken = json.access_token;
if (accessToken) {
await sdk.env.setVar({
name: "Bearer",
value: accessToken,
secret: false,
global: true,
});
}
}
}
}Testing the Workflow
To test the workflow:
Type in an in-scope domain in the connection URL input field.
Edit the request endpoint to be in-scope.
Then, add the following body data to the response:
{"access_token":"BQA_QoGKzM2I7sqcQ5cKB0oM4F_1VjwYXyUBdFJZ63nMwbrAejF0hel0dA0Ox9IRH_IT-rbt7F7dBudUOGX-kQExt3ezVuL0OBOOXYPaTVjQ5ZpE_ybkkKNEsyIjzIwOtx_7_xhuXvdaVp0BM_Lq2empsCauwvMujhPNf0HcTG0D-zIfLx9wh465oeGk0qVPM0ypFRxRWjkzM0BVMcRzG07pNk9HT_t3cBhuXt3r57o8XqKUQXlhNhWfMNca9N2v","token_type":"Bearer","expires_in":3600,"scope":"email"}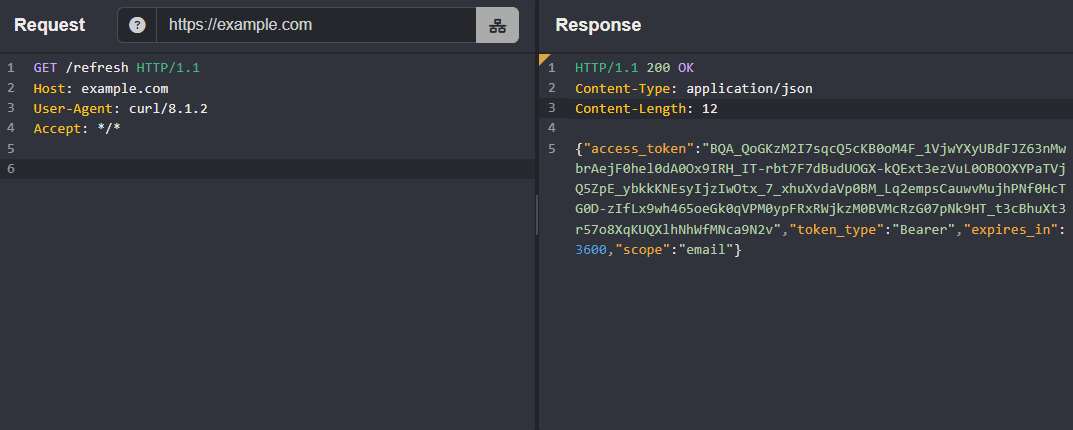
- Next, click on the
Runbutton. A message will appear notifying you that the workflow executed successfully.

The Result
To view the set environment variable, navigate to the Environment interface and refresh the Global environment by clicking on its list row.
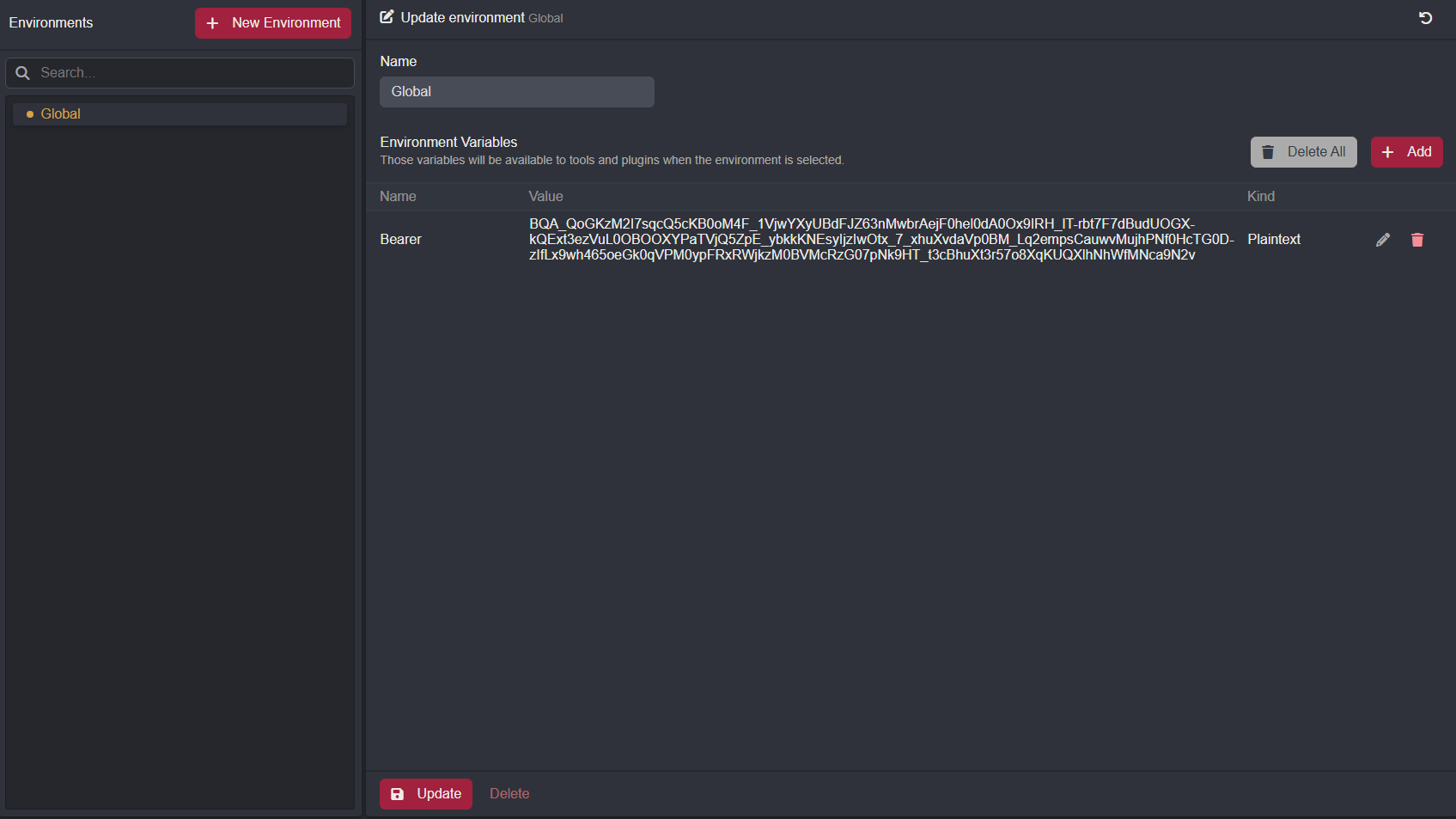
Using the Environment Variables
Now, with these workflows providing up-to-date session identifiers:
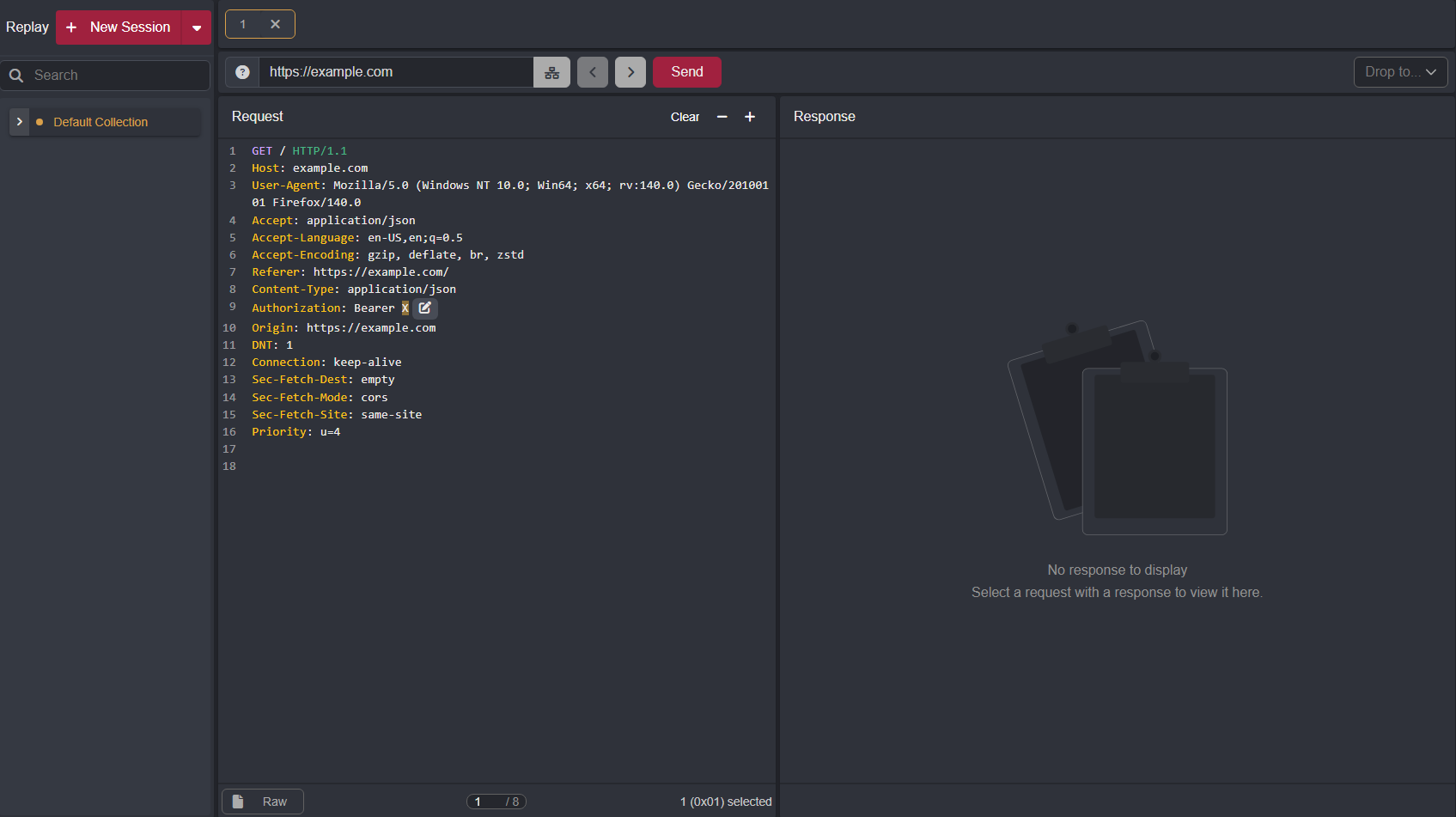
Navigate to the Replay interface.
Within a request, click, hold, and drag the left mouse button over the value you want to be replaced and click the
+button to add it as a placeholder.
Then, click on the associated edit button
of the placeholder to open thePlaceholder Settingswindow.Select
Environment Variablefrom the top drop-down menu.Select the environment variable by name from the
Environment Variabledrop-down menuThen, click on the
Addbutton to save the configuration.
The addition will be reflected in the list below.
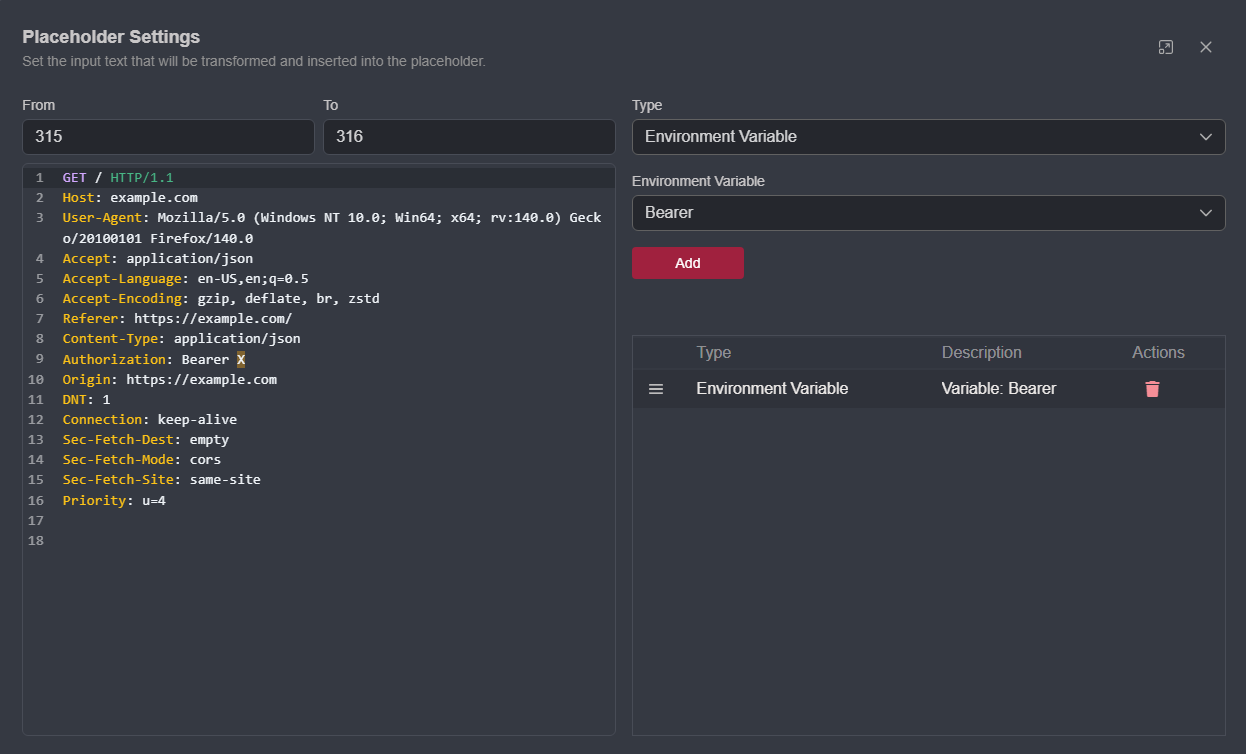
Close the settings window and send the request.
TIP
To verify the addition was successful, you can view the request by navigating to the Search interface.