HTTPQL
HTTPQL is the query language we use in Caido to let you filtering requests and responses. It is an evolving language that we hope will eventually become an industry standard.
TIP
The development of Fields is ongoing. Let us know which ones you need!
Primitives
The constructing primitives of HTTPQL Filter Clause, in order of position, are the:
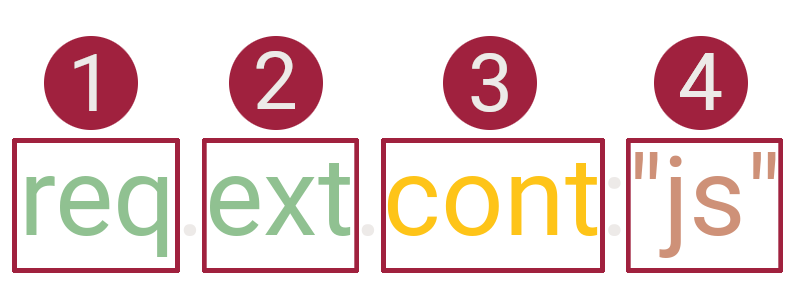
Namespace
The Namespaces that Caido supports include:
req: HTTP requests.resp: HTTP responses.preset: Filter Presets.row: A table row.source: The Caido feature source.
INFO
- The
presetandsourceNamespaces do not have aFieldor anOperator. View Exception Values for usage. - The
sourceNamespace is available in Search.
Field
The Fields that Caido supports include:
req
ext: The file extension (if present). Extensions in Caido always contain the leading.(such as.js).host: The hostname of the target server.method: The HTTP Method used for the request in uppercase. If the request is malformed, this will contain the bytes read until the first whitespace.path: The path of the query, including the extension.port: The port of the target server.raw: The full raw data of the request. This allows you to search by elements that Caido currently does not index (such as headers).created_at: The date and time the request was sent.
TIP
Caido is liberal in what is accepted as an extension.
resp
code: The status code of the reponse. If the response is malformed, this will contain everything afterHTTP/1.1and the following whitespace.raw: The full raw data of the response. This allows you to search by elements that Caido currently does not index (such as headers).roundtrip: The total time taken (in milliseconds) for the request to travel from the client to the server and for the response to travel back from the server to the client.
row
id: The numerical ID of a table row.
Operator and Value
The Value types and associated Operators that Caido supports include:
Integers
These Operators work on Fields that are numerical (port, code, roundtrip and id).
eq: Equal to the supplied value.gt: Greater than the supplied value.gte: Greater than or equal to the supplied value.lt: Less than the supplied value.lte: Less than or equal to the supplied value.ne: Not equal to the supplied value.
String/Bytes
These Operators work on Fields that are text or byte values (ext, host, method, path, query and raw).
cont: Contains the supplied value.eq: Equal to the supplied value.like: The SQLite LIKE Operator.ncont: Does not contain the supplied value.ne: Not equal to the supplied value.nlike: The SQLite NOT LIKE Operator.
TIPS
- The
contandncontOperators are case insensitive. - In SQLite - the
%character matches zero or more characters (such as%.jsto match.map.js) and the_character matches one character (such asv_lueto matchvAlue). - The
likeOperator is case sensitive for unicode characters that are beyond the ASCII range.
Regex
These Operators work on Fields that are text or byte values (that are text or byte values (ext, host, method, path, query and raw_).
regex: Matches the regex/value.+/.nregex: Doesn't match the regex/value.+/.
INFO
Not all regex features are currently supported by Caido (such as look-ahead expressions) as they are not included in the regex library of Rust.
TIP
Visit https://regex101.com/ and select Rust syntax for assistance in creating expressions.
Date/Time
These Operators work on the created_at Field.
gt: Greater than the supplied value.lt: Less than the supplied value.
The supported time formats for the values used with created_at Operators are:
- RFC3339 - example: 2024-06-24T17:03:48+00:00
- ISO 8601 - example: 2024-06-24T17:03:48+0000
- RFC2822 - example: Mon, 24 Jun 2024 17:03:48 +0000
- RFC7231 - example: Mon, 24 Jun 2024 17:03:48 GMT
- ISO9075 - example: 2024-06-24T17:03:48Z
Standalone
Caido supports standalone string values. This serves as a search shortcut as the Namespace, Field and Operator do not have to be provided.
Using a standalone string (such as "my value") will search across both requests and responses. The supplied string is replaced at runtime by:
(req.raw.cont:"my value" OR resp.raw.cont:"my value")Exception Values
preset
When using the preset Namespace - the value can be reference by either the Name or the Alias of the Preset:
- Name:
preset:"Preset name". - Alias:
preset:preset-alias.
View the Filters documentation for more information.
source
intercept- Traffic that has been proxied by Caido.replay- Traffic generated by sending requests using Replay.automate- Traffic generated by an Automate campaign.workflow- Traffic generated by a Workflow.
INFO
Autocomplete is not currently available when using the source Namespace.
TIP
- When using the
sourceNamespace - use all lowercase characters when naming the desired Caido feature. - If you are not receiving results of a
sourcequery - click theAdvancedsettings button next to the HTTPQL query bar to ensure the desiredSourcesare enabled.
Queries

Queries are composed of multiple Filter Clauses that are combined together using Logical Operators and Logical Grouping.
Logical Operators
We offer two Logical Operators:
- AND: Both the left and right clauses must be true.
- OR: Either the left or right clause must be true.
INFO
Operators can be written in upper or lower case. Both have the same priority.
Logical Grouping
Caido supports the priority of operations, AND has a higher priority than OR. Here are some examples:
clause1 AND clause2 OR clause3is equivalent to((clause1 AND clause2) OR clause3).clause1 OR clause2 AND clause3is equivalent to(clause1 OR (clause2 AND clause3)).clause1 AND clause2 AND clause3is equivalent to((clause1 AND clause2) AND clause3).
TIP
We still recommend that you insert parentheses to make sure the Logicial Groups represent what you are trying to accomplish.
