Convert Nodes
Here you'll find the list of Nodes available to use in your Convert Workflows.
WARNING
This page is currently under construction. We're working on adding more detailed documentation for each Node.
JavaScript
The JavaScript Code Node allows you to run custom scripts in your Workflows. They have a minimal code editor available in the properties pane.
When a JavaScript Node is executed inside a Workflow, the run function will be triggered.
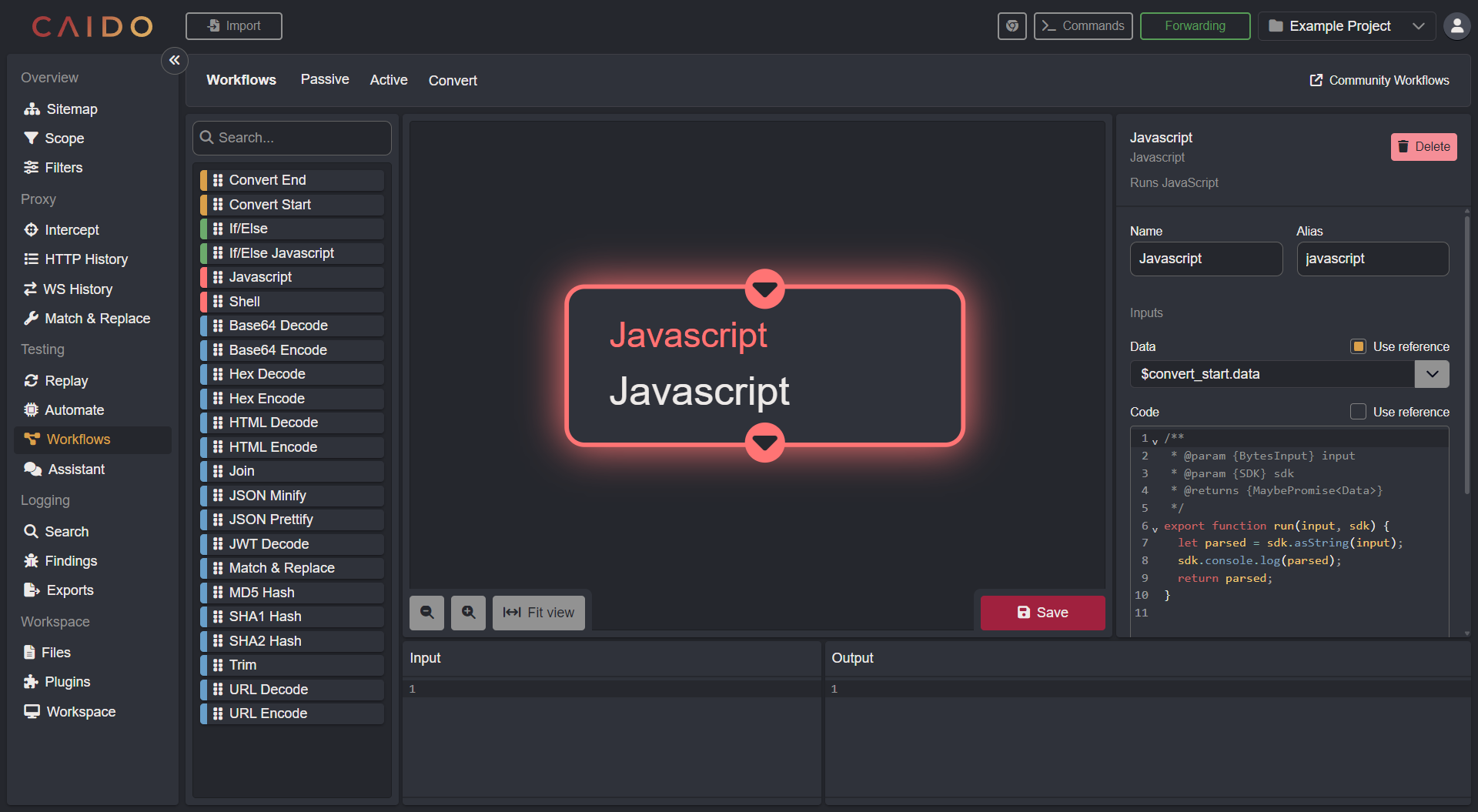
This function will take the input and sdk input parameters:
export function run(input, sdk) {
let parsed = sdk.asString(input);
sdk.console.log(parsed);
return parsed;
}The sdk parameter is an object that supplies various functionality for the Caido JS Node SDK.
INFO
Below you will find a summary of its various functions, but for now, just know that sdk.console.log() is a way to output data for debugging to the Caido Log File.
The input object is a BytesInput object, which is essentially an array of number objects which represent the Unicode codepoints of the selected text over each index of the user supplied input.
For example:
export function run(input, sdk) {
sdk.console.log(input)
...
}Where the selected input was aaa will result in:
2024-05-26T12:14:13.115630Z INFO executor:0|arbiter:3 JsSdk: [ 97, 97, 97 ]being outputed to the backend logs since the Unicode codepoint for a is 97.
In order to get the String version of the input, we use the sdk.asString function which will convert each byte of the array into its String character conterpart:
let parsed = sdk.asString(input);From there you can perform various operations on the input.
TIP
Additional functionality of sdk:
sdk.asString- convertBytesInputobject to String.sdk.console- access to JS console functionality.sdk.console.log- log data to the console.sdk.console.warn- log warning data to the console.sdk.console.debug- log debug data to the console.sdk.console.error- log error data to the console.sdk.console.requests- access to the SDK for the Requests service.sdk.console.requests.inScope- determine whether the current request is in scope or not
Shell
The Shell Node allows you to call external programs in the Workflow.
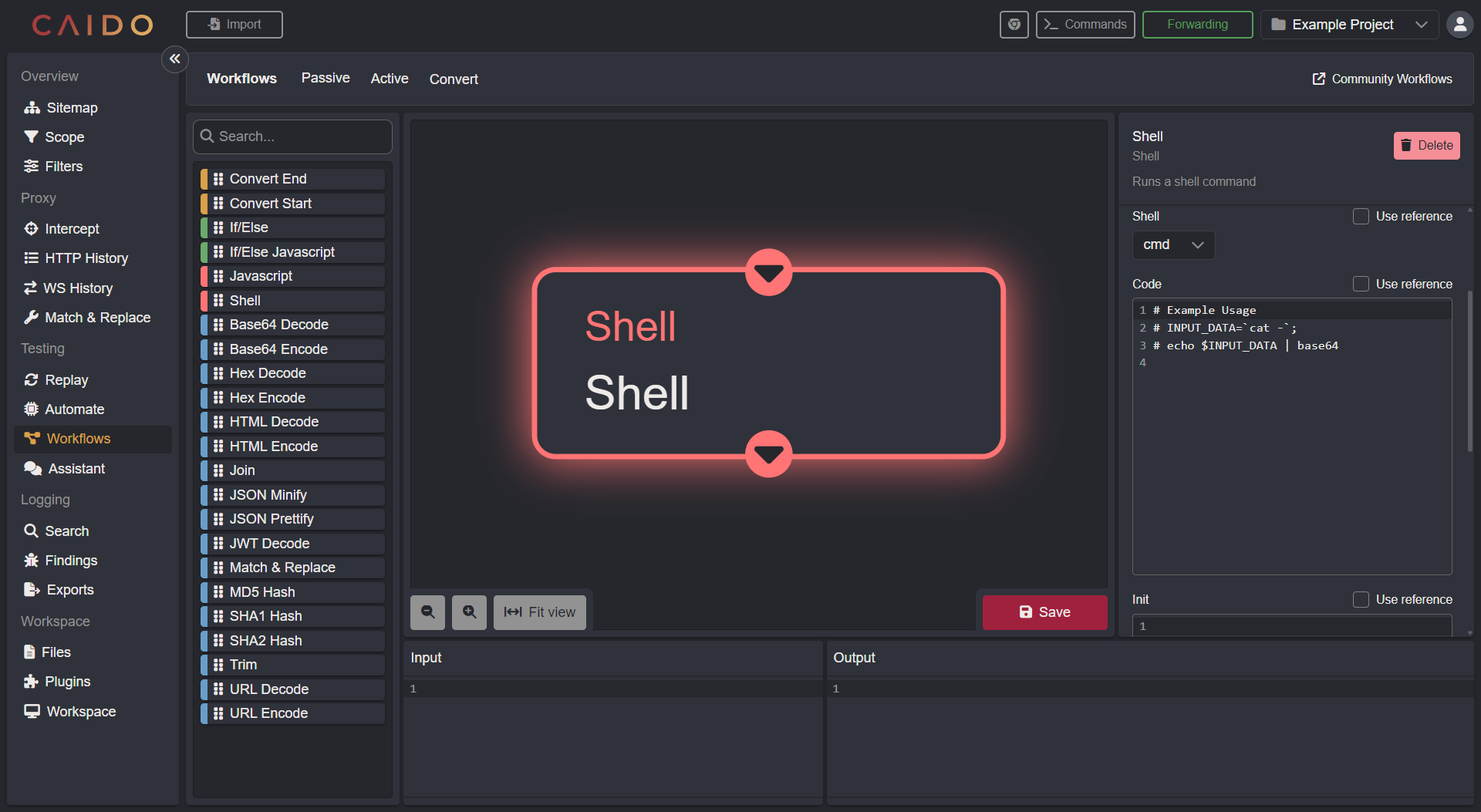
Depending on the platform on which Caido is running (Unix/Windows/MacOS) you will have access to different shells:
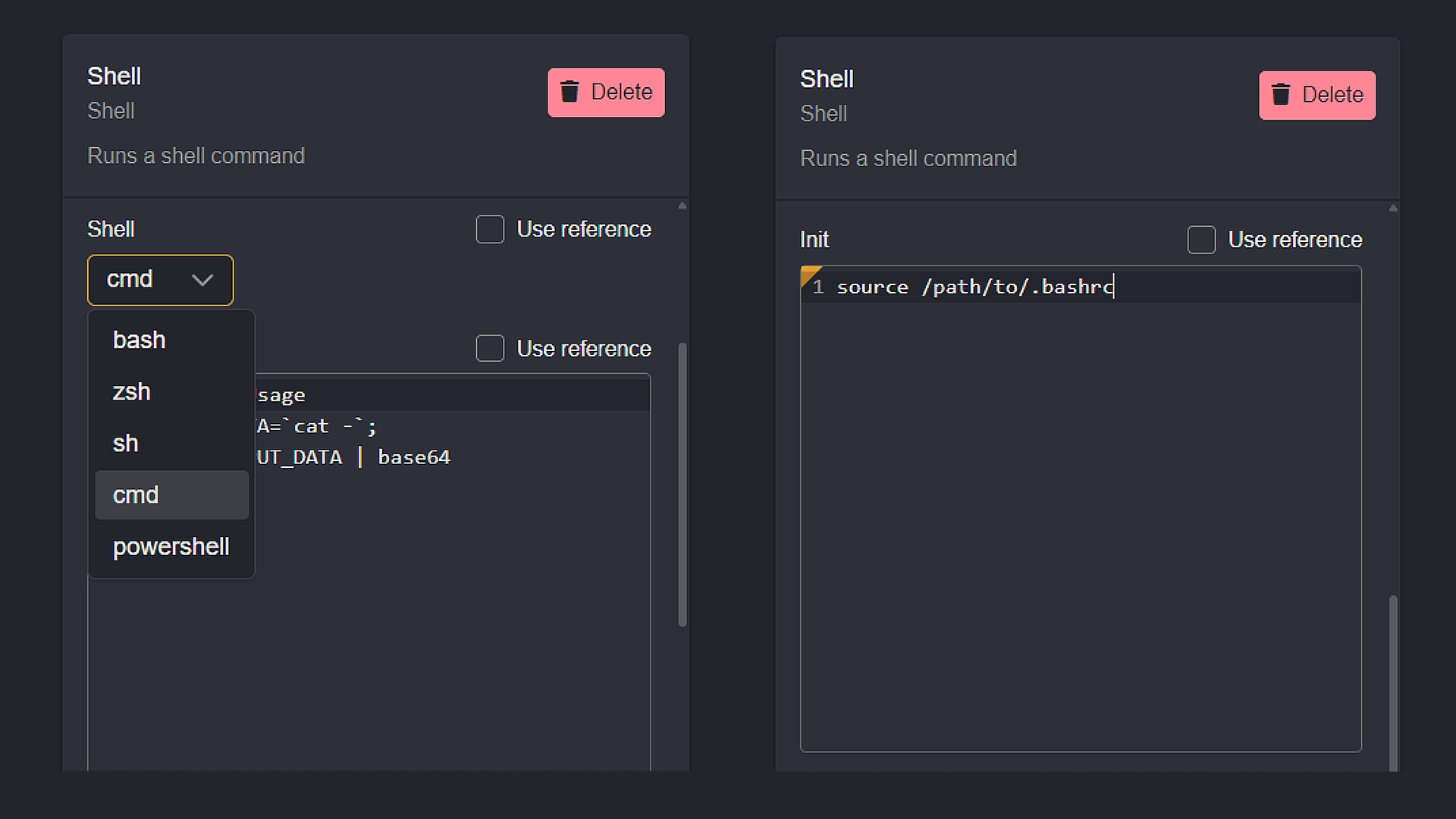
- Select your shell from the drop-down menu.
- For some shells, Caido will try to source the default
.[shell]rcfile in your home directory. If that doesn't work for you, you can manually override theInit.
Data is received via STDIN and is expected to output on STDOUT. The STDERR will be printed in the backend logs. The command should also exit with 0.
TIP
If you're running Caido on Windows and you'd like to call out to WSL for the shell node from powershell, add the following in the init section of the node:
$Env:WSLENV = ($Env:WSLENV + ":" + ((Get-ChildItem Env: | Where-Object { $_.Name -like 'CAIDO_*' }).Name -join ":")).Trim(":")Which will pass through all CAIDO_ environmental variables to WSL. Then, when making calls in the code section, perform the calls like this:
wsl -- 'echo' '$CAIDO_URL' '>' '/tmp/fun'
wsl -- 'cat' '/tmp/fun'Note the single quotes are important as they prevent Powershell from expanding the variables inside the single quotes as Powershell variables instead of bash variables inside WSL.
STDIN is also passed through to WSL by default, so that should be accessible via ’cat’ ‘-’ as it normally would be.
Since it is a bit cumbersome to write everything with single quotes around it, we recommend just running a shell script from the code section and performing all your bash actions inside that script.
If/Else
The If/Else Node can split the Workflow into two paths of action - based on the Boolean evalutation of a previous Node.
If/Else JavaScript
The If/Else Javascript Node is very similar to the JavaScript Code Node, with the exception that it must return a Boolean value.
export function run(input, sdk) {
return false;
}