HTTPQL
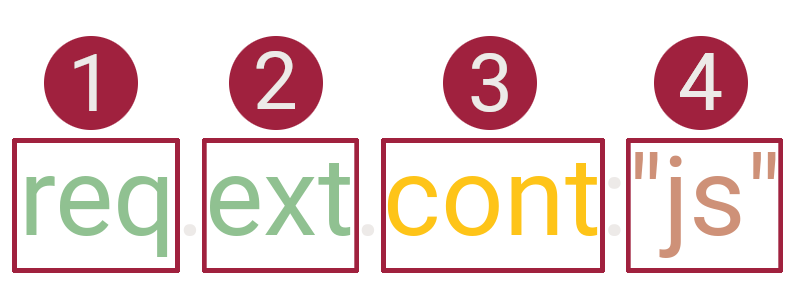
HTTPQL is the query language used in Caido that gives you the ability to filter traffic. The constructing primitives of an HTTPQL query statement, in order of position, are the:
TIP
The development of fields is ongoing. To request a field, submit a templated issue.
Namespaces
INFO
Namespaces are project-specific.
| Namespace | Description |
|---|---|
req | All proxied HTTP requests. |
resp | All proxied HTTP responses. |
preset | Filter presets. |
row | A request's numerical identifier in the traffic tables. |
source | The Caido feature source (only available in the Search interface). |
NOTE
The preset and source namespaces do not have any fields available and instead take direct values.
Fields
req
| Available Fields | Description | Value Type |
|---|---|---|
created_at | The date and time the request was sent. | Date/Time: RFC3339 (2024-06-24T17:03:48+00:00) / ISO 8601 (2024-06-24T17:03:48+0000) / RFC2822 (Mon, 24 Jun 2024 17:03:48 +0000) / RFC7231 (Mon, 24 Jun 2024 17:03:48 GMT) / ISO9075 (2024-06-24T17:03:48Z) |
ext | The extension of the requested file. | String/Byte |
host | The value of the request's Host header. | String/Byte |
len | The request size in bytes (includes request line, headers, and body data). | Integer |
method | The HTTP method used for the request. | String/Byte |
path | The URL path (includes files). | String/Byte |
port | The port of the target server. | Integer |
query | The URL query string (excludes the leading ?). | String/Byte |
raw | The full raw data of the request (includes request line, headers, and body data). | String/Byte |
tls | If the connection used TLS/SSL encryption. | Boolean (true/false) |
resp
| Available Fields | Description | Value Type |
|---|---|---|
code | The status code of the reponse. | Integer |
len | The response size in bytes (includes response line, headers, and body data). | Integer |
raw | The full raw data of the response (includes response line, headers, and body data). | String/Byte |
roundtrip | The total request/response cycle time (in milliseconds). | Integer |
row
| Available Field | Description | Value Type |
|---|---|---|
id | The numerical identifier of a request's traffic table row. | Integer |
Operators
| Operator | Description | Value Type | Additional Details |
|---|---|---|---|
eq | Equal to the supplied value. | String/Byte, Integer | Case sensitive. Requires leading . character for ext field. |
gt | Greater than the supplied value. | Date/Time, Integer | |
gte | Greater than or equal to the supplied value. | Integer | |
lt | Less than the supplied value. | Date/Time, Integer | |
lte | Less than or equal to the supplied value. | Integer | |
ne | Not equal to the supplied value. | String/Byte, Integer | Case sensitive. Requires leading . character for ext field. |
cont | Contains the supplied value. | String/Byte | Case insensitive. |
like | The SQLite LIKE Operator. | String/Byte | Case sensitive for Unicode characters beyond the ASCII range. |
ncont | Does not contain the supplied value. | String/Byte | Case insensitive. |
nlike | The SQLite NOT LIKE Operator. | String/Byte | Case sensitive for Unicode characters beyond the ASCII range. |
regex | Matches to the regular expression. | String/Byte | Rust-flavored syntax. |
nregex | Does not match to the regular expression. | String/Byte | Rust-flavored syntax. |
TIP
In SQLite - the % character matches zero or more characters (%.js matches .map.js) and the _ character matches one character (v_lue matches vAlue). Visit https://regex101.com/ and select Rust syntax to test regular expressions.
NOTE
Not all regex features are currently supported by Caido (such as look-ahead expressions) as they are not included in the regex library of Rust.
Values
preset
| Available Values | Example |
|---|---|
| A filter preset's alias. | preset:"no-images" |
| A filter preset's name. | preset:"No Images" |
source
| Available Values | Additional Details | Example |
|---|---|---|
automate, intercept, plugin, replay, workflow | Requires lowercase. Autocomplete is not supported. | source:"plugin" |
NOTE
The source namespace is only available in the Search interface. If no results are returned, ensure the inclusion of the source is enabled in the Advanced options menu.
TIP
Entering a string (such as "my value") into the HTTPQL input field will search across both requests and responses. The supplied string is replaced at runtime by:
(req.raw.cont:"my value" OR resp.raw.cont:"my value")Combining Statements
Query statements can be combined together using logical operators and logical grouping.

Logical Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| AND | Both the left and right clauses must be true. |
| OR | Either the left or right clause must be true. |
INFO
Operators are case insensitive. Both have the same priority.
Logical Grouping
Caido supports the priority of operations: AND has a higher priority than OR.
<Clause1> AND <Clause2> OR <Clause3>is equivalent to((<Clause1> AND <Clause2>) OR <Clause3>).<Clause1> OR <Clause2> AND <Clause3>is equivalent to(<Clause1> OR (<Clause2> AND <Clause3>)).<Clause1> AND <Clause2> AND <Clause3>is equivalent to((<Clause1> AND <Clause2>) AND <Clause3>).
TIP
While parentheses are optional, we recommend using them to make your logical grouping clear.
Comments
Caido supports both single-line and multi-line comments in HTTPQL queries.
TIP
Comments can be used to write descriptions or temporary disable certain query statements.


