Proxying WSL Traffic
To send traffic generated by WSL to the Caido desktop application running on your Windows host, select Export from the CA Certificate Management options.
Then, change the listening address of the Caido desktop application to All interfaces (0.0.0.0).
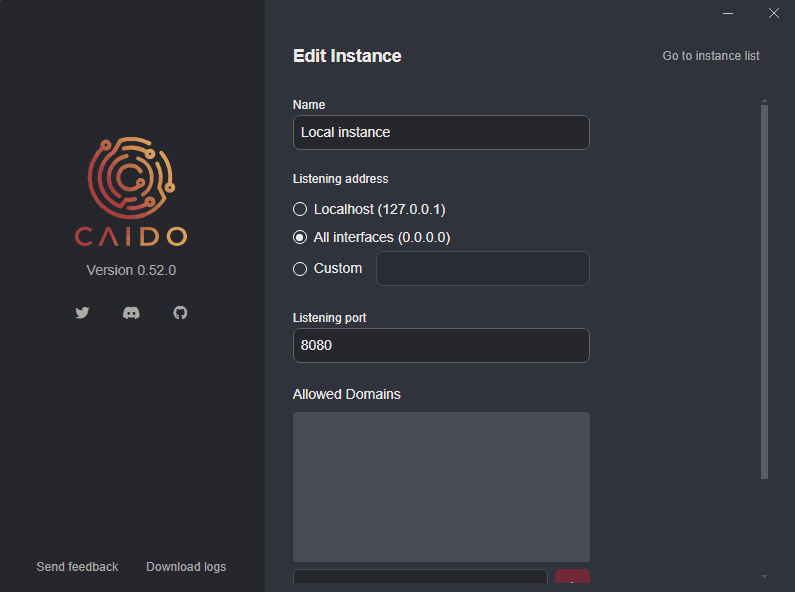
Once the address is updated, ensure to close both Caido windows.
The next time Caido is launched, you may encounter a Windows Security prompt box. Click the Allow button to allow incoming connections.
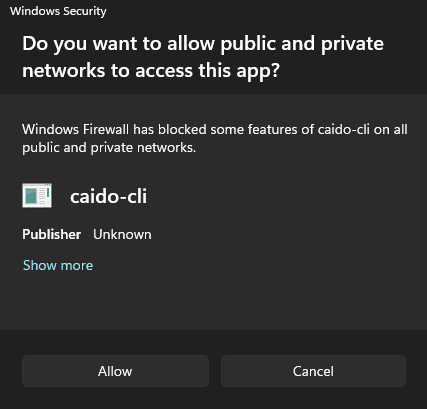
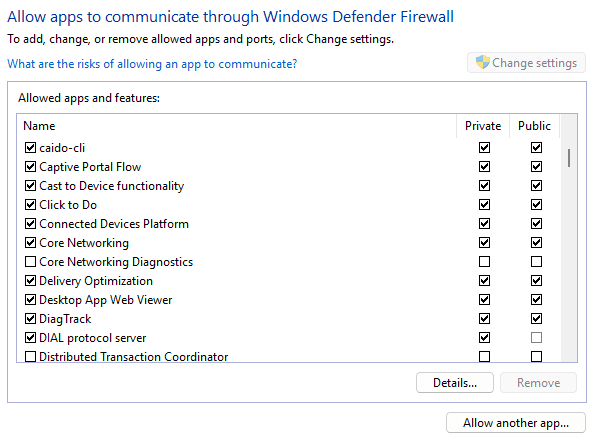
To configure the firewall rule manually:
- Open Windows Defender Firewall.
- Click on "Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall".
- Click on the
Change settingsbutton, click on thecaido-clicheckbox to grant permission, and ensure thePrivateandPubliccheckboxes are selected. - Then click on
OKto update and save the configuration.
WSL
In WSL, copy the exported CA certificate from Windows:
cp /mnt/c/Users/ninje/Downloads/ca.crt ~/ca.crtThen, install the ca.crt file system-wide and update the certificate store with:
sudo cp ~/ca.crt /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ca.crt && sudo update-ca-certificatesTo obtain the gateway IP address of your Windows host that Caido is listening on from WSL's perspective, enter:
ip route show | grep -i default | awk '{ print $3}'To test the network access, launch the Caido desktop application and issue a curl request with the -x <address:port> command-line option:
curl -x 172.22.0.1:8080 https://example.comOnce the request is sent, you should see it within in the HTTP History traffic table.
Proxy Configuration
To configure your WSL CLI tools to proxy traffic through Caido, set the http_proxy and https_proxy environment variables to the listening address/port of the desktop application:
export http_proxy="http://172.22.0.1:8080" && export https_proxy="http://172.22.0.1:8080"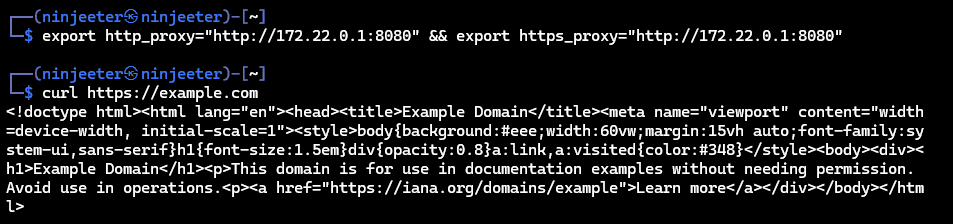
TIPS
- To verify the rules exist, use:
echo $http_proxy && echo $https_proxy - To remove the rules, use:
unset http_proxy && unset https_proxy - Consider adding these environment variables to your
~/.bashrcfile to make them permanent with:echo 'export http_proxy="http://172.22.0.1:8080"' >> ~/.bashrc && echo 'export https_proxy="http://172.22.0.1:8080"' >> ~/.bashrc - To remove both environment variables, use the following command and then close and reopen WSL:
sed -i '/export.*_proxy=/d' ~/.bashrc
